Team leader William Bourguet and Albane Le Maire

Nuclear receptors (NRs) are master regulators of gene expression in humans. Their biological functions depend on their ability to bind other molecules such as ligands (hormones, vitamins, etc.), DNA and transcriptional coregulators. They are also the primary targets of many environmental endocrine disruptors that mimic the action of endogenous ligands and cause a wide range of diseases. A major interest of the group is to reach a detailed understanding of the mechanisms involved in the (de)regulation of nuclear receptor signaling.
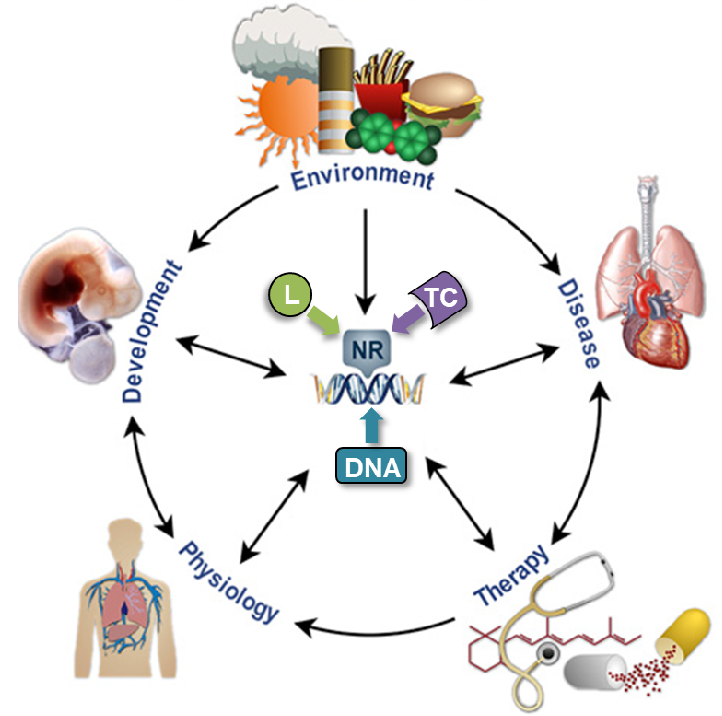
The research work of the team is organized into 5 major thematic areas:
- Mechanisms of gene regulation by nuclear receptors
- Novel nuclear receptor-based therapeutic strategies
- Nuclear receptors as targets of environmental endocrine disruptors
- Structure and function of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (ATIP-Avenir Gruszczyk)
- Lipids homeostasis
Financial support:

Scientific awards: