HS AFM
| Service |
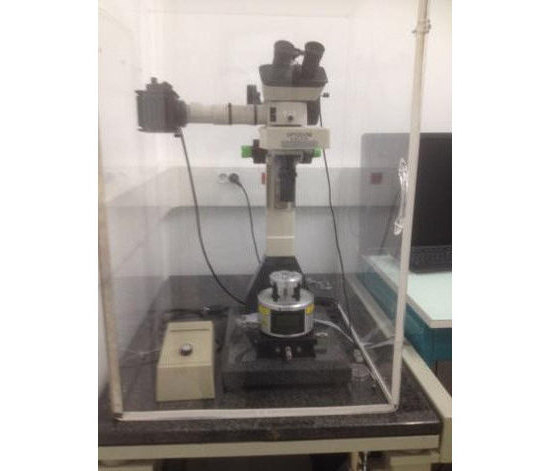
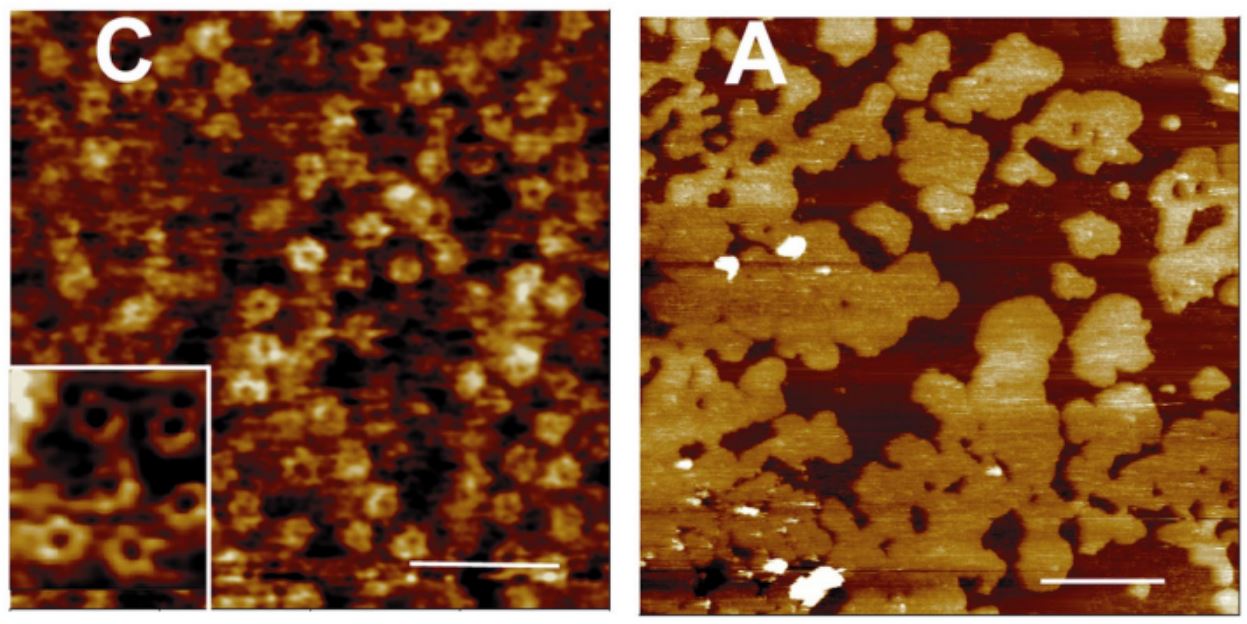
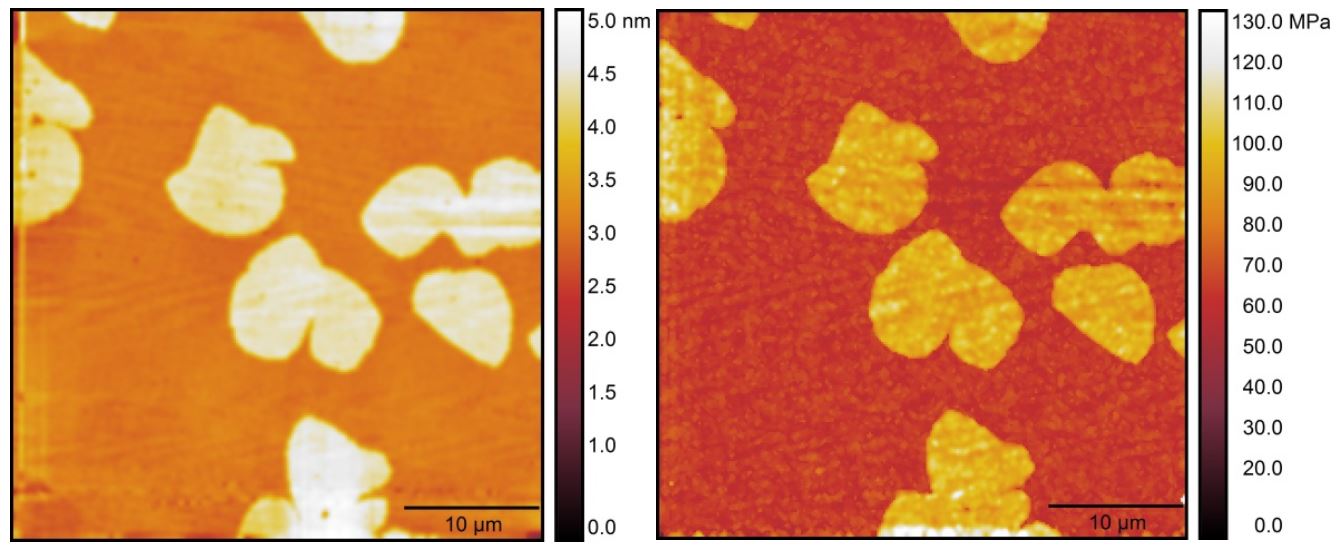
High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy
|
|
| Goal |
Real-time visualization of biomolecules activity at high spatial-temporal resolution by High-Speed AFM (HS-AFM). |
|
|
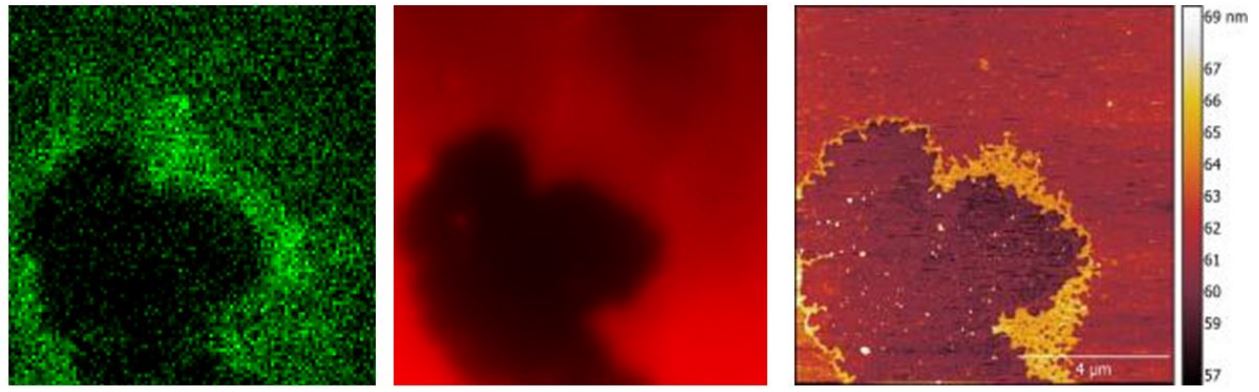
Our HS-AFM can acquire AFM images up to 10 images/seconds, allowing for dynamic tracking of slow biomolecules activity. |
||
|
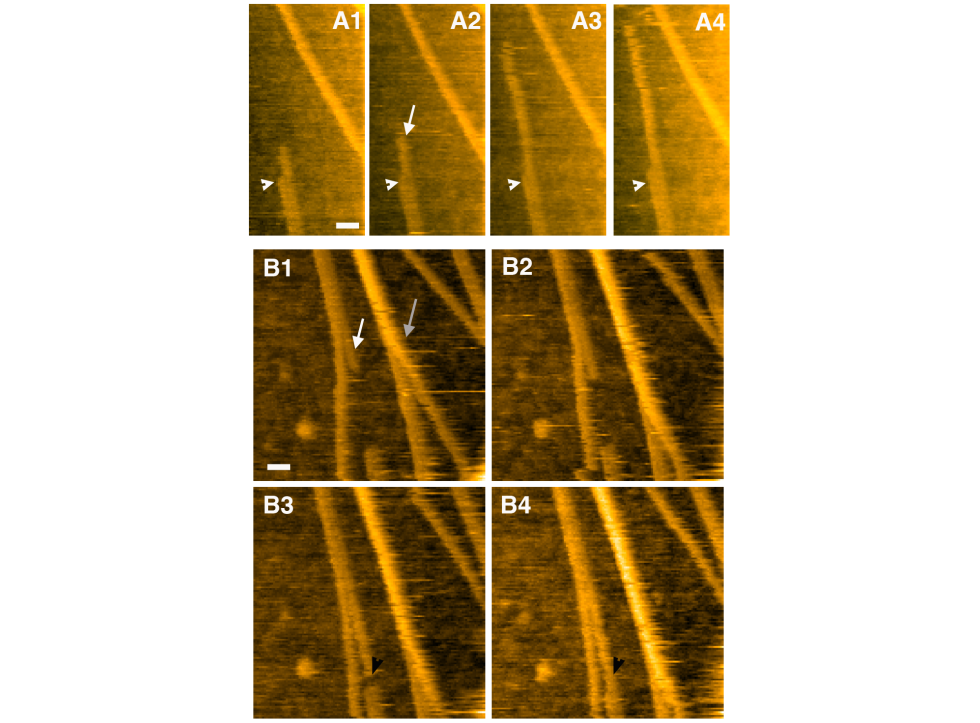
Elongation of single protofibril (white arrows) is shown in time lapses. Deciphering the Structure, Growth and Assembly of Amyloid-Like Fibrils Using High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy. Milhiet, P. E., Yamamoto, D., Berthoumieu, O., Dosset, P., Le Grimellec, C., Verdier, J. M., ... & Ando, T. (2010). PLoS One, 5(10), e13240. Speed = 1 image/second. |
||
| Equipement |
High-Speed AFM
|
||||
 |